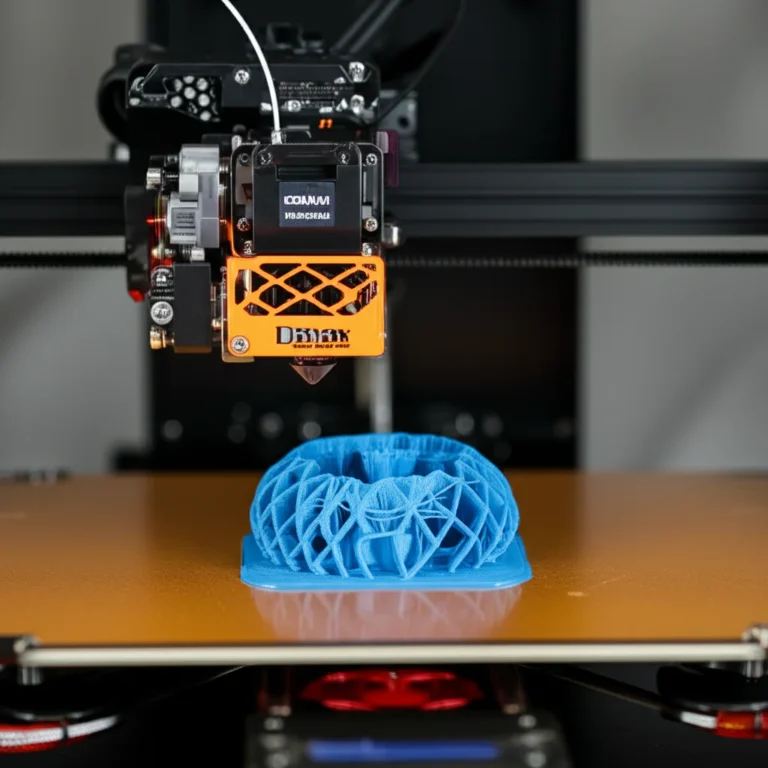
Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
What Are the 12 Most Common 3D Printing Uses in 2025? 🚀
Ever wondered how 3D printing went from sci-fi fantasy to a powerhouse technology reshaping everything from healthcare to haute cuisine? At 3D Printed™, we’ve seen firsthand how this magical layer-by-layer process is transforming industries and hobbies alike. Whether you’re curious about printing your own prosthetic limb, a custom car part, or even edible chocolate art, this guide uncovers the 12 most common and fascinating uses of 3D printing in 2025 — and trust us, some will surprise you!
Stick around as we unravel the secrets behind the materials, printers, and applications that make 3D printing a must-have tool for innovators, educators, artists, and everyday makers. Plus, we’ll share insider tips on choosing the right printer and how to avoid common pitfalls. Ready to unlock the full potential of 3D printing? Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing is revolutionizing industries like healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and even food with custom, on-demand manufacturing.
- The top 12 uses include prototyping, personalized prosthetics, architectural models, and creative arts — each leveraging unique materials and technologies.
- Choosing the right printer technology (FDM, SLA, SLS) and materials (PLA, resin, metal powders) is critical for success.
- 3D printing offers sustainability benefits through reduced waste and localized production.
- Beginners and pros alike can benefit from community resources and sample parts to get hands-on experience.
👉 Shop Popular 3D Printers & Materials:
- Prusa i3 MK3S+ on Thingiverse | Prusa Official Website
- Formlabs Form 3 SLA Printer on Thingiverse | Formlabs Official Website
- Ultimaker S5 on Thingiverse | Ultimaker Official Website
Dive deeper into the world of 3D printing with us and start creating your future today!
Table of Contents
- Quick Tips and Facts About Common 3D Printing Uses 🛠️
- The Evolution of 3D Printing: From Concept to Commonplace 🚀
- How Does 3D Printing Actually Work? A Simple Breakdown 🔍
- Top 12 Most Common 3D Printing Applications Across Industries 🌍
- Materials Matter: Choosing the Right 3D Printing Filament and Resin 🎨
- How to Pick the Perfect 3D Printer for Your Specific Use Case 🖨️
- 3D Printing in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Medicine and Prosthetics 🏥
- 3D Printing for Automotive and Aerospace: Speeding Innovation ✈️🚗
- Creative and Artistic Uses of 3D Printing: From Jewelry to Sculptures 🎭
- Education and Prototyping: How 3D Printing Fuels Innovation in Schools and Startups 🎓💡
- Industrial Manufacturing and Tooling: Boosting Efficiency with 3D Printing ⚙️
- Food and Culinary Arts: Yes, You Can 3D Print Your Dinner! 🍫🍴
- Sustainability and 3D Printing: Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Trends 🌱
- Troubleshooting Common Challenges in 3D Printing Applications 🛠️❗
- How Much Does 3D Printing Cost for Different Uses? Budgeting Tips 💰
- 3D Printing Resources and Communities: Where to Learn and Share 📚🌐
- Request a 3D Printed Sample Part: Try Before You Buy! 🎁
- Conclusion: The Future of 3D Printing Uses Is Bright and Boundless 🌟
- Recommended Links for Deep Diving into 3D Printing Uses 🔗
- Frequently Asked Questions About 3D Printing Applications ❓
- Reference Links and Further Reading 📖
Quick Tips and Facts About Common 3D Printing Uses 🛠️
- Did you know the first 3D printer was invented way back in 1983? 🤯 Talk about ahead of its time!
- From prototypes to prosthetics, 3D printing is revolutionizing industries from healthcare to aerospace. 🚀
- The most common 3D printing material? That’s plastic, but metals like titanium are gaining ground fast. 💪
- Ever dreamed of printing your own house? 🏠 It’s closer than you think! Check out our article about How Much Does a 3D Printed Home Cost? 7 Key Insights for 2025 🏡.
The Evolution of 3D Printing: From Concept to Commonplace 🚀
The journey of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, began in the 1980s. What started as a niche technology for rapid prototyping has exploded into a global phenomenon transforming industries from healthcare to aerospace.
The Early Days: A Revolution Begins
The first 3D printing technology, Stereolithography (SLA), was pioneered by Chuck Hull in 1983. Early 3D printers were expensive, complex, and limited to industrial applications.
The Rise of Desktop 3D Printing
The early 2000s saw the emergence of affordable desktop 3D printers, like those using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This democratized the technology, putting it in the hands of hobbyists, entrepreneurs, and educators.
3D Printing Today: A World of Possibilities
Today, 3D printing is more accessible and versatile than ever. Advanced materials, sophisticated software, and a thriving community of makers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
How Does 3D Printing Actually Work? A Simple Breakdown 🔍
Imagine building a sculpture with LEGOs, brick by tiny brick. That’s the basic idea behind 3D printing! Here’s a simplified look:
- Design: It all starts with a digital 3D model, created using 3D design software.
- Slicing: The 3D model is sliced into hundreds or thousands of thin layers by specialized software.
- Printing: The 3D printer deposits or cures material layer by layer, following the sliced design, until the object is complete.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the technology and material, the printed object may require cleaning, curing, or removal of support structures.
Top 12 Most Common 3D Printing Applications Across Industries 🌍
- Prototyping: Quickly create physical models to test designs, ergonomics, and functionality.
- Manufacturing: Produce end-use parts, from custom tooling to complex components, on demand.
- Healthcare: Create anatomical models for surgical planning, personalized prosthetics, and medical devices.
- Aerospace: Manufacture lightweight, high-performance parts for aircraft, spacecraft, and drones.
- Automotive: Produce prototypes, tooling, and even end-use parts for cars and motorcycles.
- Architecture: Create architectural models and even full-scale building components.
- Education: Enhance STEM learning with hands-on projects, from robotics to design thinking.
- Art and Design: Produce sculptures, jewelry, fashion accessories, and custom home decor.
- Food Printing: Create intricate chocolate designs, personalized candies, and even experimental dishes.
- Dental: Produce dental models, surgical guides, aligners, and even temporary restorations.
- Consumer Goods: Create custom phone cases, personalized gifts, toys, and household items.
- Research and Development: Explore new materials, processes, and applications in various fields.
Materials Matter: Choosing the Right 3D Printing Filament and Resin 🎨
The material you choose will depend on your specific application, budget, and desired properties. Here’s a quick look at some popular options:
Filaments (Used in FDM Printers)
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable, easy to print, good for prototypes and basic models.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Strong, impact-resistant, good for functional prototypes and durable parts.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Durable, chemical-resistant, good for food-safe applications.
- Nylon: Strong, flexible, good for gears, hinges, and wear-resistant parts.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible, rubber-like, good for phone cases, wearables, and shock-absorbing parts.
Resins (Used in SLA and Other Resin-Based Printers)
- Standard Resins: Offer a balance of detail, strength, and affordability.
- Engineering Resins: Provide high strength, heat resistance, or other specialized properties.
- Castable Resins: Designed for creating molds for jewelry making and other casting applications.
- Dental and Medical Resins: Biocompatible and safe for use in dental and medical applications.
How to Pick the Perfect 3D Printer for Your Specific Use Case 🖨️
Choosing the right 3D printer can feel overwhelming. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Printing Technology: FDM printers are affordable and versatile, while SLA printers offer higher resolution and smoother finishes.
- Build Volume: How large do your prints need to be? Consider the printer’s build volume.
- Materials: What materials do you need to print with? Make sure the printer supports them.
- Resolution and Accuracy: Higher resolution means finer details. Accuracy ensures dimensional accuracy.
- Software Compatibility: Check if the printer works with your preferred 3D design and slicing software.
- Budget: Desktop 3D printers range in price from a few hundred to several thousand dollars.
3D Printing in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Medicine and Prosthetics 🏥
3D printing is transforming healthcare in remarkable ways:
- Personalized Prosthetics: Custom-designed and printed prosthetics offer improved fit, functionality, and affordability.
- Surgical Planning: 3D printed anatomical models help surgeons visualize complex procedures and improve patient outcomes.
- Medical Devices: From implants to surgical instruments, 3D printing enables the creation of patient-specific devices.
- Bioprinting: While still in its early stages, bioprinting holds the potential to create living tissues and organs.
3D Printing for Automotive and Aerospace: Speeding Innovation ✈️🚗
The automotive and aerospace industries rely on 3D printing for:
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly iterate designs and test aerodynamic properties.
- Lightweighting: Create lighter-weight components to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Customization: Produce custom parts and accessories for both consumers and manufacturers.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: Print parts on demand, reducing lead times and inventory costs.
Creative and Artistic Uses of 3D Printing: From Jewelry to Sculptures 🎭
3D printing has unleashed a wave of creativity in the art and design world:
- Sculptures and Art Installations: Artists are pushing the boundaries of form and material with 3D printed sculptures.
- Jewelry Design: Create intricate designs, prototypes, and even final pieces using castable resins and metals.
- Fashion Accessories: From shoes to handbags, 3D printing enables the creation of unique and personalized fashion items.
- Custom Home Decor: Print vases, lamps, wall art, and other decorative items to personalize your living space.
Education and Prototyping: How 3D Printing Fuels Innovation in Schools and Startups 🎓💡
3D printing is a powerful tool for education and prototyping:
- Hands-on Learning: Students can design, print, and test their ideas, fostering creativity and problem-solving skills.
- STEM Education: 3D printing brings STEM concepts to life, from engineering to robotics.
- Rapid Prototyping for Startups: Quickly create prototypes to test ideas, secure funding, and bring products to market faster.
- Maker Spaces and Fab Labs: 3D printers are essential tools in maker spaces, fostering collaboration and innovation.
Industrial Manufacturing and Tooling: Boosting Efficiency with 3D Printing ⚙️
3D printing is transforming industrial manufacturing:
- Custom Tooling: Create jigs, fixtures, and other tooling in-house, reducing lead times and costs.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: Print parts on demand, eliminating the need for large inventories and minimizing waste.
- Complex Geometries: Manufacture parts with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional methods.
- Lightweighting and Material Efficiency: Optimize designs for weight and material usage, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Food and Culinary Arts: Yes, You Can 3D Print Your Dinner! 🍫🍴
While still an emerging application, 3D food printing is gaining traction:
- Decorative Elements: Create intricate chocolate designs, personalized candies, and edible decorations for cakes and pastries.
- Customized Nutrition: Tailor food textures and nutrient profiles for individuals with dietary restrictions or medical conditions.
- Experimental Cuisine: Chefs are exploring the creative potential of 3D food printing to create innovative dishes and culinary experiences.
Sustainability and 3D Printing: Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Trends 🌱
3D printing offers several sustainability advantages:
- Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing uses only the material needed, minimizing waste compared to subtractive methods.
- On-Demand Production: Print parts only when needed, reducing overproduction and transportation-related emissions.
- Local Manufacturing: 3D printing enables localized production, reducing reliance on global supply chains and their associated environmental impacts.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of biodegradable and recycled materials in 3D printing is increasing.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges in 3D Printing Applications 🛠️❗
While 3D printing is becoming more accessible, you might encounter some bumps along the way:
- Print Bed Adhesion Issues: Prints warping or failing to stick to the print bed? Experiment with different bed adhesion techniques like glue sticks, tapes, or rafts.
- Stringing/Oozing: Unwanted strings of plastic between parts? Adjust retraction settings or try a filament with lower stringing tendencies.
- Clogged Nozzles: Filament not extruding properly? A clogged nozzle is a common culprit. Learn how to clean or replace it.
- Layer Shifting: Layers appearing misaligned? Check for loose belts, a wobbly print bed, or vibrations during printing.
How Much Does 3D Printing Cost for Different Uses? Budgeting Tips 💰
The cost of 3D printing varies widely depending on factors like:
- Printing Technology: FDM printers are generally more affordable than SLA, SLS, or metal 3D printers.
- Materials: Some materials, like basic PLA filament, are very affordable, while others, like high-performance resins or metal powders, can be more expensive.
- Design Complexity and Size: Larger, more complex designs require more time and material to print, increasing costs.
- Post-Processing: Some 3D printing technologies require post-processing steps like cleaning, curing, or support removal, which can add to the overall cost.
3D Printing Resources and Communities: Where to Learn and Share 📚🌐
The 3D printing community is vast and welcoming. Here are some great resources:
- Online Communities:
- Thingiverse: A massive repository of free 3D models.
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/3Dprinting offer a wealth of information and discussions.
- Facebook Groups: Join 3D printing groups to connect with fellow enthusiasts.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and Skillshare offer 3D printing courses for all levels.
- YouTube Channels: Many YouTubers share tutorials, reviews, and project ideas related to 3D printing.
- Local Maker Spaces: Connect with other makers, access equipment, and learn new skills at your local maker space.
Request a 3D Printed Sample Part: Try Before You Buy! 🎁
Want to experience the quality and versatility of 3D printing firsthand? Contact us to request a free sample part!
Conclusion: The Future of 3D Printing Uses Is Bright and Boundless 🌟

Wow, what a ride! From humble beginnings in the 1980s to revolutionizing industries like healthcare, aerospace, and even food, 3D printing has truly become a game-changer. Whether you’re a hobbyist dreaming of printing your own custom phone case or a startup prototyping the next big thing, the versatility and accessibility of 3D printing open doors to endless possibilities.
We’ve explored the top 12 common uses, the materials that bring designs to life, and how to choose the perfect printer for your needs. Plus, we peeked into the future with innovations in bioprinting, sustainable manufacturing, and on-demand production.
Remember that choosing the right material and printer technology is key to success. For example, FDM printers are fantastic for beginners and basic prototypes, while SLA and SLS shine when you need precision and complex geometries.
If you’re itching to dive in, don’t forget to check out our offer to request a 3D printed sample part — a perfect way to feel the magic firsthand before investing.
So, what’s next? Keep exploring, keep experimenting, and keep pushing the boundaries of what you can create. The world of 3D printing is vast, vibrant, and waiting for your unique touch. Ready to print your future? We sure are! 🚀
Recommended Links for Deep Diving into 3D Printing Uses 🔗
-
👉 Shop Popular 3D Printers:
- Prusa i3 MK3S+: Thingiverse | Prusa Official Website
- Formlabs Form 3 (SLA): Thingiverse | Formlabs Official Website
- Ultimaker S5: Thingiverse | Ultimaker Official Website
-
Recommended Books on 3D Printing:
Frequently Asked Questions About 3D Printing Applications ❓
What are the most popular items to 3D print for beginners?
For beginners, simple, practical, and fun projects are the way to go. Popular starter prints include:
- Phone stands and holders: Easy to design and print, useful around the house.
- Keychains and small toys: Great for practicing basic shapes and settings.
- Cable organizers: Functional prints that help manage clutter.
- Planter pots: Simple geometry with room for creativity.
- Replacement parts: Small broken items like knobs or clips.
These projects help beginners get comfortable with printer calibration, bed adhesion, and slicing software without overwhelming complexity. Plus, they’re rewarding because you get something useful or fun right away!
How does 3D printing work and what are its applications?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer from digital 3D models using various materials like plastics, resins, or metals. The process involves:
- Designing a 3D model using CAD software.
- Slicing the model into thin layers.
- Printing each layer sequentially to build the object.
- Post-processing to clean, cure, or finish the print.
Applications span a huge range:
- Prototyping for rapid product development.
- Healthcare for prosthetics and surgical models.
- Aerospace and automotive for lightweight, complex parts.
- Education to bring STEM concepts to life.
- Art and fashion for custom designs.
- Food printing for creative culinary arts.
The versatility and customization options make 3D printing a powerful tool across industries.
What are the benefits of using 3D printing in education and hobbying?
3D printing in education and hobbying offers:
- Hands-on learning: Students engage actively by designing and printing their own projects.
- Creativity and problem-solving: Encourages innovation and iterative design thinking.
- Accessibility: Desktop printers make 3D printing affordable and approachable.
- Interdisciplinary learning: Combines engineering, art, math, and technology.
- Community building: Maker spaces and online forums foster collaboration and sharing.
For hobbyists, it opens up endless possibilities to create custom tools, models, and gifts, making the learning curve fun and rewarding.
What are some creative and useful things to 3D print at home?
At home, 3D printing can be both practical and playful. Some favorites include:
- Custom kitchen gadgets: Cookie cutters, measuring spoons, spice racks.
- Home organization: Drawer dividers, hooks, cable clips.
- Replacement parts: Broken knobs, clips, or missing pieces.
- Personalized gifts: Keychains, jewelry, figurines.
- Board game accessories: Custom tokens, dice holders, card organizers.
The beauty is in customization — you can tailor designs to your exact needs or style, making your home truly one-of-a-kind.
Reference Links and Further Reading 📖
- Formlabs: 3D Printing Technologies and Applications
- Xometry: Applications of 3D Printing
- Dassault Systèmes: Most Common Materials Used for 3D Printing
- Prusa Research Official Website
- Ultimaker Official Website
- Thingiverse: Free 3D Models
- 3D Printed™ Category: 3D Printable Objects
- 3D Printed™ Category: 3D Printing Innovations
- 3D Printed™ Category: 3D Design Software
- 3D Printed™ Category: 3D Printing in Education