Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
What is 3D Printing? 25+ Real Examples & How It Works! 🚀
Ever watched a plastic dragon emerge from a buzzing box, layer by layer, like magic? That’s 3D printing—and it’s so much more than just toys and trinkets. From custom prosthetic limbs to edible pizzas and even full-sized houses, 3D printing is quietly (and not-so-quietly) reshaping our world. In fact, did you know the global 3D printing market is projected to hit $41 billion by 2026? That’s a lot of dragons, dentures, and designer shoes!
Whether you’re a curious newbie, a DIY enthusiast, or just wondering what all the hype is about, this guide will walk you through exactly what 3D printing is, how it works, and over 25 jaw-dropping real-world examples. We’ll spill our best tips, biggest fails, and why you might want to start printing your own phone stand—or your next meal. Ready to see what’s possible? Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing builds objects layer by layer from digital designs, using materials like plastic, metal, and even food.
- It’s everywhere: From medical marvels (prosthetics, implants) to art, fashion, automotive, aerospace, and even construction.
- Beginner-friendly and advanced options exist—FDM printers (like Prusa, Creality) are great for most, while resin and metal printers serve pros.
- Customization, rapid prototyping, and sustainability are huge advantages, but there’s a learning curve (and occasional spaghetti monsters).
- The future is wild: Think bioprinting organs, printing houses, and personalized everything.
👉 Shop Top 3D Printers:
Find 3D Models to Print:
Ready to discover what you can print next? Keep reading for the full scoop and our favorite real-life examples!
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts
- 🕰️ The Evolution of 3D Printing: From Sci-Fi to Your Desk
- 🔬 What Exactly Is 3D Printing? (Additive Manufacturing Demystified)
- 🛠️ How Does 3D Printing Work? Step-by-Step Guide
- 🏭 3D Printing in Industry: Disrupting Manufacturing and Beyond
- 1. 🏡 Everyday Examples of 3D Printing You’ll Actually Recognize
- 2. 🏥 Medical Marvels: 3D Printing in Healthcare
- 3. 🚗 Automotive and Aerospace: 3D Printing on the Fast Track
- 4. 🏗️ Architecture & Construction: Building the Future Layer by Layer
- 5. 🎨 Art, Fashion, and Food: Creative Uses of 3D Printing
- 6. 🧩 Education & DIY: 3D Printing for Learning and Fun
- 🧪 Types of 3D Printing Technologies and Processes Explained
- 🧱 Materials Used in 3D Printing: Plastics, Metals, and Beyond
- 🖨️ Choosing a 3D Printer: What to Know Before You Buy
- 💡 Tips, Tricks, and Common Mistakes in 3D Printing
- 🌍 Environmental Impact and Sustainability of 3D Printing
- 🚀 The Future of 3D Printing: Trends to Watch
- Conclusion
- Recommended Links
- FAQ
- Reference Links
⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts
- 3D printing = additive manufacturing. It builds objects layer by layer from a digital file. If you’re still picturing a Star Trek replicator, you’re not far off! Learn more about what is a 3D printed item.
- It’s everywhere: From prosthetics to pizza, 3D printing is revolutionizing industries.
- You don’t need to be a rocket scientist (but rocket scientists use it too!): Hobbyists, students, and pros all use 3D printers.
- 3D printers use many materials: Plastics, metals, ceramics, even chocolate!
- The global 3D printing market is projected to hit $41 billion by 2026 (3DPrinting.com). That’s a lot of layers!
- Designs can be downloaded from sites like Thingiverse or created from scratch with free software like Tinkercad.
- Not just for prototypes: 3D printing is used for end-use parts, art, fashion, and even houses.
- Curious what you can print? Check out our 3D Printable Objects category for inspiration.
🕰️ The Evolution of 3D Printing: From Sci-Fi to Your Desk
Let’s hop in our DeLorean and take a quick trip through 3D printing history. Spoiler: It’s not as new as you think!
The Early Days: From Concept to Reality
- 1981: Hideo Kodama invents the first rapid prototyping system in Japan.
- 1984: Charles Hull invents stereolithography (SLA), the OG of 3D printing (source).
- 1990s: Stratasys (Scott Crump) brings FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) to market, making 3D printing more accessible.
From Industrial Secret to Desktop Revolution
- 2005: The RepRap project launches, aiming for a self-replicating 3D printer. Cue the open-source explosion!
- 2010s: Desktop 3D printers like MakerBot and Prusa i3 start popping up in homes, schools, and hackerspaces.
- Today: 3D printing is everywhere—from prosthetic limbs to printed houses.
Why the Sudden Boom?
- Open-source hardware/software
- Falling costs
- Expanding materials
- Growing online communities (hello, Reddit’s r/3Dprinting)
Fun Fact: The first 3D printed object? A tiny cup, printed by Charles Hull. We’ve come a long way from plastic shot glasses!
🔬 What Exactly Is 3D Printing? (Additive Manufacturing Demystified)
If you’ve ever wondered, “What is 3D printing, really?”—you’re not alone! Let’s break it down.
The Basics
- 3D printing = Additive manufacturing: It creates objects by adding material layer by layer, as opposed to subtractive manufacturing (think: carving a statue from a block).
- Digital to physical: You start with a digital 3D model, then the printer brings it to life.
“Machines build parts and products one layer at a time. You can make pretty much anything you can dream up with 3D printers.” — Xometry
Key Ingredients
- A 3D Model: Designed in software (CAD) or downloaded from Thingiverse.
- Slicing Software: Converts the model into printable layers (G-code).
- The Printer: Follows the G-code to build your object, layer by layer.
Why Additive Manufacturing Rocks
- Complex shapes? No problem! Print objects impossible to make with traditional methods.
- Less waste: Only use what you need.
- Customization: Make one-of-a-kind items, from custom-fit shoes to personalized phone cases.
Want to see what’s possible? Check out our 3D Printing Innovations section.
🛠️ How Does 3D Printing Work? Step-by-Step Guide
Ready for a peek behind the curtain? Here’s how we go from “I want that!” to “I made that!” in the world of 3D printing.
Step 1: Design Your Model
- Create your own: Use free tools like Tinkercad (great for beginners) or advanced options like Fusion 360.
- Download a model: Sites like Thingiverse, MyMiniFactory, and Cults3D are treasure troves.
Step 2: Slice It Up
- Slicing software (e.g., Ultimaker Cura, PrusaSlicer) converts your model into “slices”—thin layers the printer can understand.
- Adjust settings: Layer height, infill, supports, and more.
Step 3: Prep the Printer
- Load your material: Filament (PLA, ABS, PETG, etc.), resin, or powder—depending on your printer.
- Level the bed: Trust us, you’ll want to get this right. (Ask us about the time we forgot—hello, spaghetti monster!)
Step 4: Print!
- Send the file to your printer via SD card, USB, or Wi-Fi.
- Watch the magic: The printer builds your object, layer by layer. (Pro tip: The first few layers are crucial.)
Step 5: Post-Processing
- Remove supports: Carefully snip away any extra material.
- Finishing touches: Sand, paint, or assemble as needed.
Step-by-Step Table
| Step | What You Need | Pro Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Design | CAD software or 3D model | Start simple—think keychains, not Iron Man suit |
| Slice | Slicer software | Preview layers to catch errors early |
| Prep Printer | Filament/resin, clean bed | Level, level, level! |
| SD card/USB/Wi-Fi | Watch the first layer like a hawk | |
| Post-Process | Tools, sandpaper, paint | Take your time for best results |
Want to dive deeper? Explore our 3D Design Software reviews.
🏭 3D Printing in Industry: Disrupting Manufacturing and Beyond
3D printing isn’t just for hobbyists and cosplayers—big industries are cashing in, too.
Manufacturing’s Secret Weapon
- Rapid prototyping: Design, print, test, repeat—no need for expensive molds.
- On-demand production: Print spare parts as needed, reducing inventory and waste (3DPrinting.com).
- Complex geometries: Create parts that are lighter, stronger, and impossible to make with traditional methods.
Industry Adoption
- Aerospace: GE, Boeing, and Relativity Space are printing engine parts and even rockets (source).
- Automotive: Ford and BMW use 3D printing for tools, jigs, and end-use parts.
- Healthcare: 99% of hearing aids are 3D printed (3DPrinting.com).
- Construction: 3D printed houses are a reality—check out ICON’s projects.
Market Growth
- Forecast: The global 3D printing market is expected to reach $41 billion by 2026 (3DPrinting.com).
- Why? Flexibility, speed, and cost savings.
Curious about the latest breakthroughs? Visit our 3D Printing Innovations hub.
1. 🏡 Everyday Examples of 3D Printing You’ll Actually Recognize
Let’s get real—what can you actually print? Here are some everyday examples that might surprise you.
Household Items
- Phone stands, cable organizers, planters: Check Thingiverse for endless ideas.
- Replacement parts: Lost a knob or a hook? Print a new one in minutes.
Consumer Products
- Footwear: Adidas 4D uses 3D printed midsoles for custom comfort (Adidas 4D on Adidas Official).
- Eyewear: 3D printed frames are stylish and sustainable (3DPrinting.com).
Toys and Games
- Board game pieces, puzzles, figurines: The limit is your imagination (and your printer’s build volume).
Jewelry and Accessories
- Custom rings, bracelets, and pendants: Get creative with unique designs.
Want more ideas? Explore our 3D Printable Objects for inspiration.
2. 🏥 Medical Marvels: 3D Printing in Healthcare
If you think 3D printing is just for plastic trinkets, think again. It’s literally saving lives!
Prosthetics and Implants
- Custom prosthetics: Affordable, tailored limbs for kids and adults (Xometry).
- Implants: Hip cups like LimaCorporate’s Delta-TT Cup mimic bone structure and last for years (3DPrinting.com).
Dental and Hearing Aids
- Dental aligners, crowns, dentures: Most are now 3D printed for perfect fit.
- Hearing aids: 99% are made with additive manufacturing.
Bioprinting and Pharmaceuticals
- Tissue engineering: Printing living cells for organs and skin grafts (still experimental, but promising).
- 3D printed drugs: Spritam® is the first FDA-approved 3D printed pill (source).
Personal Story: We once printed a custom splint for a friend’s broken finger—faster and cheaper than waiting for a traditional cast!
3. 🚗 Automotive and Aerospace: 3D Printing on the Fast Track
Buckle up—these industries are going full throttle with 3D printing!
Automotive
- Spare parts on demand: No more waiting weeks for a tiny bracket—print it in hours (3DPrinting.com).
- Prototyping: Rapid iteration for new car models.
- Tools and jigs: Custom tools for assembly lines.
Aerospace
- Lightweight, complex parts: GE printed a turbine frame, reducing part count from 150 to 1 and cutting mass by 30% (3DPrinting.com).
- Space exploration: Relativity Space printed a rocket (Terran-1) and launched it into orbit (Relativity Space).
Table: Automotive vs. Aerospace 3D Printing
| Industry | Uses | Benefits | Brands/Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Parts, tools, protos | Speed, cost, customization | Ford, BMW, Local Motors |
| Aerospace | Engine parts, rockets | Weight savings, complexity | GE, Boeing, Relativity |
Want to print your own car parts? Search Thingiverse for inspiration.
4. 🏗️ Architecture & Construction: Building the Future Layer by Layer
Think 3D printing is just for small stuff? Think again—entire buildings are going up, one layer at a time!
3D Printed Houses
- Concrete printers: Companies like ICON and Apis Cor are printing homes in days, not months.
- Disaster relief: Rapidly build shelters after natural disasters (Xometry).
Architectural Models
- Scale models: Architects print detailed models to wow clients and test ideas.
Benefits
- Speed: Houses in 24 hours? Yes, please.
- Customization: Unique designs, less waste, lower costs.
Curious about the wildest builds? Check out our 3D Printing Innovations for jaw-dropping projects.
5. 🎨 Art, Fashion, and Food: Creative Uses of 3D Printing
3D printing isn’t just practical—it’s downright artsy (and tasty)!
Art and Sculpture
- Custom sculptures: Artists like Joshua Harker push boundaries with intricate, impossible shapes (Joshua Harker’s work).
- Movie props: Hollywood uses 3D printing for costumes and set pieces (3DPrinting.com).
Fashion
- Wearable art: Designers like Iris van Herpen use 3D printing for futuristic runway looks (Iris van Herpen).
- Jewelry: Unique, customizable pieces.
Food
- Edible prints: Print chocolate, pizza, or even plant-based meat (source).
- Personalized nutrition: Pills or snacks tailored to your needs.
Want to print your own art? Explore MyMiniFactory for creative models.
6. 🧩 Education & DIY: 3D Printing for Learning and Fun
Let’s get hands-on! 3D printing is a game-changer in classrooms and maker spaces.
Learning by Doing
- STEM projects: Print models of molecules, organs, or historical artifacts (3D Printing in Education).
- Tactile learning: Great for visualizing complex concepts.
DIY and Maker Culture
- Hobby projects: From cosplay props to drone parts, the sky’s the limit.
- Community sharing: Sites like Thingiverse and Cults3D let you share and remix designs.
Personal Anecdote
We once hosted a school workshop where kids printed their own name tags—and the excitement was off the charts! (Pro tip: Always bring extra filament.)
🧪 Types of 3D Printing Technologies and Processes Explained
Not all 3D printers are created equal. Here’s a quick tour of the main types—each with its own superpowers.
Table: 3D Printing Technologies
| Technology | How It Works | Best For | Example Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM/FFF | Melts & extrudes plastic filament | Prototypes, hobby, education | Prusa, Creality |
| SLA/DLP/CLIP | Cures liquid resin with light | High detail, jewelry, dental | Formlabs, Anycubic |
| SLS/DMLS/MJF | Fuses powder with laser/inkjet | Industrial, functional parts | HP, EOS, 3D Systems |
| Binder Jetting | Glues powder with binder | Full-color models, sand cores | ExOne, Desktop Metal |
| Material Jetting | Jets droplets, cured by UV | Multi-material, high detail | Stratasys, Objet |
| Directed Energy Deposition | Melts metal wire/powder with laser | Large metal parts, repair | Optomec, Sciaky |
FDM/FFF (Fused Deposition Modeling/Fused Filament Fabrication)
- Most common for hobbyists.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use, wide material selection.
- Cons: Lower resolution than resin printers.
SLA/DLP/CLIP (Resin Printing)
- Uses light to cure resin.
- Pros: High detail, smooth surfaces.
- Cons: Messy, resin can be smelly.
SLS/DMLS/MJF (Powder Bed Fusion)
- Uses lasers or inkjets to fuse powder.
- Pros: Strong, functional parts; no supports needed.
- Cons: Expensive, industrial use.
Want to compare printers? Check our 3D Printer Reviews.
🧱 Materials Used in 3D Printing: Plastics, Metals, and Beyond
What’s in your print? Let’s break down the materials that make 3D printing so versatile.
Plastics
- PLA: Easy, eco-friendly, perfect for beginners (learn more).
- ABS: Tough, heat-resistant, but can warp.
- PETG: Combines strength and flexibility.
Specialty Filaments
- Flexible (TPU): Bendable, great for phone cases.
- Wood/metal/carbon fiber blends: For unique looks and properties.
Resins
- Standard: For high-detail prints.
- Dental/biocompatible: For medical applications.
Metals
- Stainless steel, titanium, aluminum: Used in aerospace, automotive, and medical implants (3DPrinting.com).
Other Materials
- Ceramics, concrete, food, even living cells!
Table: Material Comparison
| Material | Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Easy, eco-friendly | Brittle, low temp | Prototypes, toys |
| ABS | Strong, heat-resistant | Warps, fumes | Tools, enclosures |
| PETG | Tough, flexible | Can string | Bottles, parts |
| Resin | High detail | Messy, toxic | Jewelry, dental |
| Metal | Strong, durable | Expensive, industrial | Implants, engines |
Want to see what’s possible? Browse our 3D Printable Objects for material inspiration.
🖨️ Choosing a 3D Printer: What to Know Before You Buy
Thinking of joining the 3D printing revolution? Here’s what to consider before you buy your first (or next) printer.
Rating Table: What Matters Most
| Aspect | Importance (1-10) | Our Take |
|---|---|---|
| Print Quality | 9 | Crisp details make all the difference |
| Ease of Use | 8 | Don’t fight your printer—enjoy it! |
| Reliability | 10 | Nothing’s worse than a failed print |
| Community | 8 | Support makes troubleshooting easier |
| Material Range | 7 | More options = more creativity |
| Upgradeability | 7 | Mods keep things fresh |
FDM vs. Resin: Which Should You Choose?
- FDM/FFF: Great for beginners, affordable, versatile.
- Resin (SLA/DLP): High detail, perfect for miniatures and jewelry.
Popular Brands
- Prusa: Beloved for reliability and community (Prusa Official).
- Creality: Budget-friendly, modder’s dream (Creality Official).
- Anycubic: Resin specialists (Anycubic Official).
- Formlabs: Professional resin printers (Formlabs Official).
👉 CHECK PRICE on:
- Prusa: Amazon | eBay | Prusa Official
- Creality: Amazon | eBay | Creality Official
- Anycubic: Amazon | eBay | Anycubic Official
- Formlabs: Amazon | Formlabs Official
Our Tips
- Start simple: Don’t buy the fanciest machine right away.
- Check the community: Active forums = easier troubleshooting.
- Think about what you want to print: Miniatures? Go resin. Big parts? FDM.
Ready to compare? Dive into our 3D Printer Reviews.
💡 Tips, Tricks, and Common Mistakes in 3D Printing
We’ve made every mistake in the book—so you don’t have to. Here’s what we wish we knew when we started.
Quick Tips
- Level your bed. Seriously. It’s the #1 cause of failed prints.
- Use good filament. Cheap stuff = headaches.
- Watch the first layer. If it’s not sticking, stop and fix it.
Common Mistakes
- Overcomplicating your first print: Start with something simple.
- Ignoring maintenance: Clean your nozzle and bed regularly.
- Skipping supports: Some designs need them—don’t skip!
Pro Tricks
- Upgrade your slicer settings: Play with infill, supports, and speed.
- Try different materials: Each has its quirks and charms.
- Join a community: Reddit, Facebook groups, and our own 3D Printing Innovations section are goldmines.
Want more troubleshooting tips? Check our 3D Printable Objects for guides and hacks.
🌍 Environmental Impact and Sustainability of 3D Printing
Is 3D printing green? Well, it’s complicated—but promising!
The Good
- Less waste: Additive manufacturing uses only what’s needed (3DPrinting.com).
- On-demand production: Reduces overproduction and inventory.
- Biodegradable materials: PLA is plant-based and compostable.
The Bad
- Energy use: Some printers (especially industrial) use lots of power.
- Plastic waste: Failed prints and supports can add up.
The Hopeful
- Recycled filaments: Brands like Reflow and Filabot turn waste into new filament.
- Local manufacturing: Print what you need, where you need it—reducing shipping emissions.
Table: Sustainability Pros & Cons
| Aspect | ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Waste | Minimal scrap | Support material waste |
| Materials | Biodegradable options | Not all are recyclable |
| Energy | Efficient for small runs | High for large/metal |
Want to print greener? Explore our 3D Printing Innovations for eco-friendly ideas.
🚀 The Future of 3D Printing: Trends to Watch
What’s next for 3D printing? Grab your crystal ball—here’s what we see coming.
Bigger, Faster, Smarter
- Larger printers: Printing houses, bridges, and even rockets (Relativity Space).
- Speed improvements: New tech like CLIP and MJF are making prints faster than ever (3DPrinting.com).
- AI-powered design: Generative design tools optimize shapes for strength and efficiency.
New Materials
- Bioprinting: Printing organs and tissues for transplants.
- Food printing: Personalized nutrition, on demand.
Mass Customization
- Personalized products: Shoes, glasses, and even medicine tailored just for you.
The Bottom Line
3D printing is only getting more powerful, accessible, and creative. We can’t wait to see what you’ll make next!
Want to stay ahead of the curve? Bookmark our 3D Printing Innovations page for the latest trends.
Conclusion
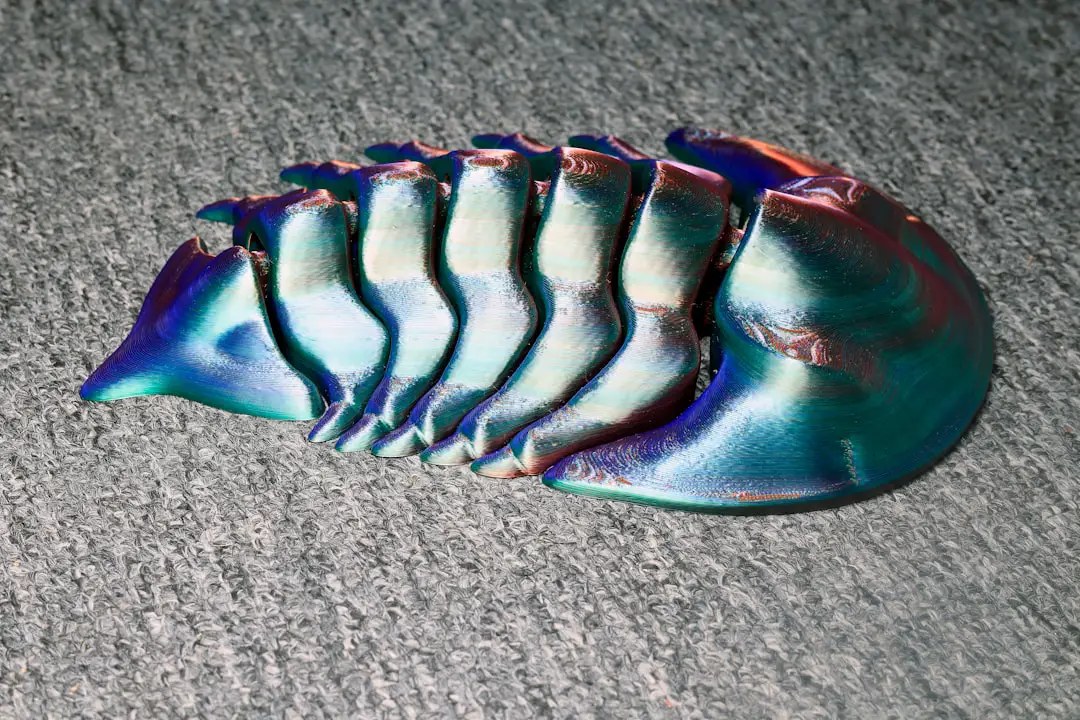

So, what is 3D printing and what are some jaw-dropping examples? If you’ve made it this far, you now know it’s not just about plastic toys or sci-fi dreams. From custom prosthetics and rocket engines to fashion, food, and even full-sized houses, 3D printing is transforming how we design, make, and interact with the world.
Positives:
✅ Unmatched versatility—print everything from phone stands to organs
✅ Rapid prototyping and customization
✅ Eco-friendly potential with less waste and biodegradable materials
✅ Accessible to hobbyists, students, and professionals alike
✅ Constantly evolving with new materials and technologies
Negatives:
❌ Some printers and materials can be pricey
❌ Steep learning curve for advanced projects
❌ Not all materials are recyclable
❌ Failed prints and troubleshooting can be frustrating (we’ve been there—spaghetti monsters, anyone?)
Our Recommendation:
If you’re curious, creative, or just love cool gadgets, jump in! Start with a beginner-friendly FDM printer, try simple projects, and join the thriving 3D printing community. Whether you want to print a missing LEGO, a custom phone case, or a prosthetic limb, the only real limit is your imagination (and maybe your print bed size).
And remember: Level your bed, use good filament, and don’t be afraid to experiment. The future is being built layer by layer—and you can be part of it!
Recommended Links
👉 Shop 3D Printers and Accessories:
- Prusa 3D Printers: Amazon | eBay | Prusa Official Website
- Creality 3D Printers: Amazon | eBay | Creality Official Website
- Anycubic 3D Printers: Amazon | eBay | Anycubic Official Website
- Formlabs Resin Printers: Amazon | Formlabs Official Website
- Adidas 4D Shoes: Adidas Official Website
- Books on 3D Printing:
Find 3D Models to Print:
Explore More on 3D Printed™:
- 3D Printable Objects
- 3D Printing Innovations
- 3D Design Software
- 3D Printer Reviews
- 3D Printing in Education
FAQ
What are the different types of 3D printing technologies available?
There are several main types, each with unique strengths:
- FDM/FFF (Fused Deposition Modeling/Fused Filament Fabrication): The most common for hobbyists. Melts plastic filament and extrudes it layer by layer. Great for prototypes, toys, and functional parts. Brands: Prusa, Creality.
- SLA/DLP/CLIP (Resin Printing): Uses light to cure liquid resin. Delivers high detail, perfect for jewelry, dental, and miniatures. Brands: Formlabs, Anycubic.
- SLS/DMLS/MJF (Powder Bed Fusion): Fuses powder (plastic or metal) with lasers or inkjets. Used for industrial, functional parts. Brands: HP, EOS.
- Binder Jetting & Material Jetting: Used for full-color models, sand cores, and multi-material prints.
- Directed Energy Deposition: Melts metal wire/powder with a laser for large or repair parts.
Learn more about types of 3D printing.
Read more about “How Does 3D Printing Work Exactly? 12 Secrets Unveiled! 🖨️ (2025)”
How does 3D printing work and what are its applications?
3D printing works by:
- Designing or downloading a 3D model.
- Slicing the model into printable layers using software.
- Printing the object layer by layer using your chosen material.
Applications include:
- Prototyping and product design
- Medical devices (prosthetics, implants, dental)
- Aerospace and automotive parts
- Architecture and construction
- Art, fashion, and food
- Education and DIY projects
It’s used everywhere from classrooms to rocket factories! (source)
Read more about “How Much Money Can You Make 3D Printing? 14+ Ways to Profit in 2025 💸”
What are some beginner-friendly 3D printing projects for hobbyists?
Start simple and build your confidence! Some great beginner projects:
- Keychains and name tags: Quick wins, easy to customize.
- Phone stands and cable organizers: Practical and forgiving.
- Mini planters or vases: Show off your green thumb.
- Replacement knobs or hooks: Useful around the house.
- Toys and figurines: Fun for all ages.
Find thousands of free models on Thingiverse and Cults3D.
Read more about “15 Epic 3D Printer Projects to Try in 2025 🚀”
What are the most popular and useful items to 3D print at home?
Some of the most popular and useful prints include:
- Household gadgets: Clips, holders, organizers, and repair parts.
- Tools: Wrenches, jigs, and custom parts.
- Toys and games: Board game pieces, puzzles, and fidget toys.
- Personal accessories: Custom phone cases, jewelry, and keychains.
- Educational models: Math, science, and anatomy aids.
Explore more ideas in our 3D Printable Objects section.
Read more about “What Are Most 3D Printed Objects Made of Today? Top 11 Materials (2025) 🛠️”
Is 3D printing environmentally friendly?
It can be! 3D printing uses only the material needed (less waste), and there are biodegradable options like PLA. However, energy use and plastic waste from failed prints/supports are concerns. Look for recycled filaments and print only what you need for a greener approach. (source)
Read more about “Is 3D printing environmentally friendly?”
What software do I need to get started with 3D printing?
- 3D Modeling: Tinkercad (beginner), Fusion 360 (advanced)
- Slicing: Ultimaker Cura, PrusaSlicer
- File formats: .STL and .OBJ are most common.
Read more about “What Is Material for 3D Printing? 12 Must-Know Types in 2025 🛠️”
Can I 3D print with metal, food, or other unusual materials?
Absolutely! Industrial printers can use metals like titanium and stainless steel for aerospace and medical parts. There are also printers for ceramics, concrete, and even food (chocolate, pizza, plant-based meat). For home use, specialty filaments can mimic wood, metal, or carbon fiber.
Read more about “2 Unusual Objects Printed with a 3D Printer That Will Blow Your Mind 🤯 (2025)”
Reference Links
- 3DPrinting.com – What is 3D Printing?
- Xometry – Applications of 3D Printing
- Built In – 3D Printing: What It Is, How It Works and Examples
- Wikipedia – 3D Printing
- Prusa Official Website
- Creality Official Website
- Formlabs Official Website
- Anycubic Official Website
- HP 3D Printing
- EOS 3D Printing
- Adidas 4D
- ICON 3D Printed Homes
- Relativity Space
- Filabot Recycled Filament
- Reflow Filament
- Joshua Harker – 3D Printed Art
- Iris van Herpen – Fashion
For even more, check out 3D Printing: What It Is, How It Works and Examples | Built In.