Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
Why 3D Printing Is So Expensive: 13 Surprising Reasons Explained 🤑 (2025)
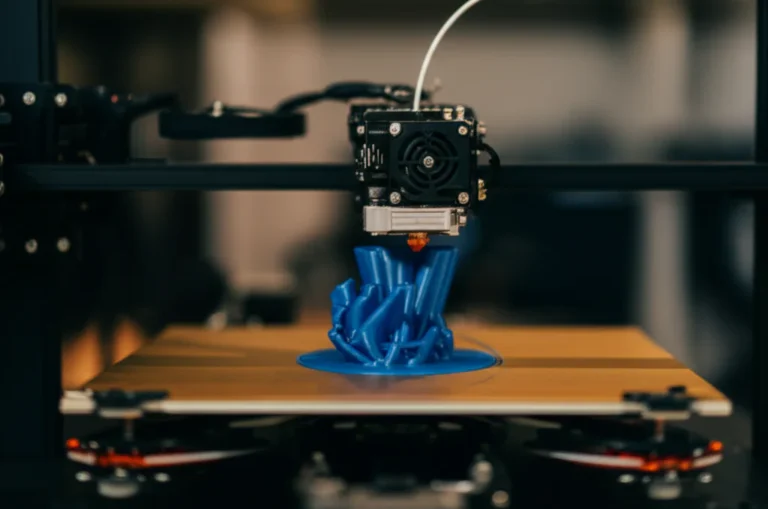
Ever stared at a 3D printer price tag and thought, “Wait, why does this cost so much?” You’re not alone! Whether you’re a curious hobbyist or a budding entrepreneur, the cost of 3D printing can feel like an enigma wrapped in a mystery filament spool. From the high-tech wizardry inside the machines to the pricey materials and hidden maintenance costs, there’s a lot more behind that number than meets the eye.
In this article, we’ll unravel 13 surprising reasons why 3D printing is so expensive, from the history of the technology to the sneaky hidden costs that catch many off guard. Plus, we’ll share expert tips from our engineers at 3D Printed™ on how to slash your expenses without sacrificing quality. Curious about how failed prints and exotic materials factor in? Or wondering if the price is really coming down? Stick around — the answers might just change how you see this revolutionary technology.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing costs are driven by complex technology, expensive materials, and ongoing maintenance. The initial printer price is just the beginning.
- Different printing technologies (FDM, SLA, SLS) have vastly different price points and material costs.
- Brand reputation and customer support add to the upfront cost but can save money and frustration long-term.
- Hidden expenses like failed prints, upgrades, and safety gear often surprise newcomers.
- Industrial 3D printing with exotic materials commands premium prices due to precision and performance needs.
- Smart strategies like choosing the right printer, optimizing slicer settings, and leveraging free software can cut costs significantly.
- 3D printing’s value shines in rapid prototyping, customization, education, and small-batch manufacturing despite the price tag.
Ready to start printing smarter? Check out our recommended budget-friendly printers and materials to kick off your 3D printing journey without breaking the bank:
- Creality Ender 3 V3 SE: Amazon | Walmart | Creality Official Website
- Sovol SV06: Amazon | Walmart | Sovol Official Website
- Elegoo Mars 3 Pro Resin Printer: Amazon | Walmart | Elegoo Official Website
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts
- 🕰️ The Genesis of Cost: A Brief History of 3D Printing Expenses
- 💰 Unpacking the Price Tag: Why Initial 3D Printer Investment Stings
- 🔄 The Never-Ending Story: Ongoing Expenses in 3D Printing
- 🏭 Beyond the Hobby Bench: Industrial vs. Consumer 3D Printing Costs
- 👻 The Stealthy Spenders: Hidden Costs You Might Not Expect
- 📉 The Great Debate: Is 3D Printing Truly Getting Cheaper?
- 🎯 When Does the Investment Pay Off? The Value Proposition of Additive Manufacturing
- 💡 Smart Spending: Practical Strategies to Slash Your 3D Printing Costs
- ✅ Conclusion: Is the Price Tag Justified?
- 🔗 Recommended Links: Your Next Steps in Affordable 3D Printing
- ❓ FAQ: Burning Questions About 3D Printing Costs Answered
- 📚 Reference Links: Dive Deeper into the Data
Here is the main body of the article, crafted by the expert team at 3D Printed™.
⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts
So, you’re eyeing that shiny new 3D printer, dreaming of all the amazing things you’ll create. But then you see the price tag and… record scratch. Why does this awesome technology feel like it costs a small fortune? Don’t worry, we’ve all been there. Before we dive deep into the rabbit hole of 3D printing economics, here are some rapid-fire insights to get you started. And if you’re wondering about the nitty-gritty of individual print costs, our guide on how much it costs per 3D print is your next click.
- It’s Not Just the Printer: The initial machine purchase is only the beginning. Think of it like buying a car; you still need to pay for gas (filaments/resin), oil changes (maintenance), and those cool fuzzy dice (upgrades).
- Technology Dictates Price: A simple Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printer that melts plastic filament can be found for less than a new smartphone. But a Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) machine that fuses nylon powder can cost more than a new car. 😲
- Material World: A standard 1kg spool of PLA filament might set you back a reasonable amount, but a kilogram of high-performance PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) can cost hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars.
- Time is Money: This is a huge one, especially for printing services. As one user on a Prusa forum wisely noted, “A lot of what you’re paying for is no doubt operator setup and time.” This includes model preparation, machine setup, post-processing, and packing.
- Failure is an Option (An Expensive One): Failed prints are a rite of passage. That beautiful 24-hour print failing at 95%? That’s not just lost time; it’s wasted material straight into the bin.
- Open-Source is Your Friend: The reason you can even buy an affordable desktop 3D printer is largely thanks to the RepRap open-source project, which kicked off a revolution in accessibility.
🕰️ The Genesis of Cost: A Brief History of 3D Printing Expenses
Ever wonder how we got here? Let’s hop in our 3D-printed DeLorean and take a trip back in time. The concept of additive manufacturing, or building things “layer by layer,” isn’t new. As the folks at 100 Concepts explain in their excellent video overview, the journey began around 1980 with Dr. Hideo Kodama’s patent for a resin-curing system. You can see their full breakdown here.
For decades, this technology was locked away in industrial labs and protected by iron-clad patents, making it astronomically expensive. The machines were colossal, the materials were proprietary, and getting anything printed required a team of engineers and a budget the size of a small country’s GDP. Traditional manufacturing, like injection molding, was the only game in town for plastics, but as the video points out, the initial tooling costs of “$15,000 – $100,000+” made it impossible for small innovators.
The real game-changer? The expiration of key patents in the late 2000s. This legal shift unleashed a tidal wave of innovation, most notably the RepRap project. Suddenly, a global community of makers, hackers, and engineers could legally create and share designs for 3D printers that could, in theory, print their own parts. This was the Big Bang for the desktop 3D printing universe, leading to the affordable machines we see today from brands like Creality and Prusa. It’s a perfect example of 3D Printing Innovations at its finest.
💰 Unpacking the Price Tag: Why Initial 3D Printer Investment Stings
Okay, so prices have come down from the stratosphere, but a good printer is still a significant investment. Let’s break down what you’re actually paying for when you buy the machine itself.
1. The Tech Under the Hood: R&D and Innovation Costs
A 3D printer isn’t just a hot glue gun on a robot arm (though, let’s be honest, some of the early ones felt like it!). Reputable companies pour immense resources into research and development. They’re refining motion systems for greater precision, developing sophisticated firmware to compensate for tiny imperfections, and creating features like automatic bed leveling and filament runout sensors that make our lives easier.
Brands like Bambu Lab have recently shaken up the industry with high-speed CoreXY printers packed with LiDAR and AI-powered failure detection. That kind of tech doesn’t come cheap. You’re paying for the salaries of brilliant engineers, the cost of prototyping, and the relentless pursuit of a machine that just works out of the box.
2. Printer Types & Their Price Points: FDM vs. SLA vs. SLS and Beyond
The biggest factor in a printer’s cost is the underlying technology. Think of it like cars: a basic sedan gets you from A to B, but a Formula 1 car is in a different league of performance and price.
| Technology | How It Works | Common Materials | Price Range (Consumer/Prosumer) | ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | Melts and extrudes a plastic filament layer by layer. | PLA, PETG, ABS, TPU | Low to Mid | Most affordable, wide material variety, easy to use. | Lower resolution, visible layer lines, weaker on Z-axis. |
| SLA/MSLA (Stereolithography) | Cures liquid resin with a UV light source (laser or LCD screen). | Standard & Engineering Resins | Mid to High | Incredible detail, smooth surfaces, isotropic strength. | Messy workflow, smelly, materials can be brittle/toxic. |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | Fuses powdered polymer with a high-power laser. | Nylon, TPU | Very High | Strong, functional parts, no support structures needed. | Extremely expensive, requires significant space & safety. |
As you can see, the jump is massive. Your trusty Creality Ender 3 is a fantastic FDM entry point. A resin printer like the Elegoo Mars series offers stunning detail for miniatures. But an SLS machine? That’s typically the domain of service bureaus and large corporations due to the five- or six-figure price tag. For a closer look at specific models, check out our 3D Printer Reviews.
3. Brand Value & Support: Are You Paying for Peace of Mind?
Why buy a Prusa MK4 when a similar-looking clone is available for a fraction of the price? The answer often comes down to one word: support.
- Reputable Brands (e.g., Prusa, Bambu Lab, UltiMaker): You’re investing in a polished ecosystem. This includes detailed documentation, 24/7 customer support, active user communities, and a warranty that the company will actually honor. Their printers often undergo rigorous quality control, meaning fewer headaches for you.
- Budget/Clone Brands: While the value can be incredible, you’re often on your own. Support might be non-existent, documentation can be poorly translated, and quality control can be a roll of the dice. You might save money upfront, but you’ll likely pay for it with your time and frustration.
We’re not saying budget printers are bad—far from it! They’ve opened the hobby to millions. But it’s crucial to understand that part of the premium for a well-known brand is for the safety net they provide.
🔄 The Never-Ending Story: Ongoing Expenses in 3D Printing
You’ve bought the printer, unboxed it, and printed your first perfect Benchy. Victory! But the journey (and the spending) has just begun.
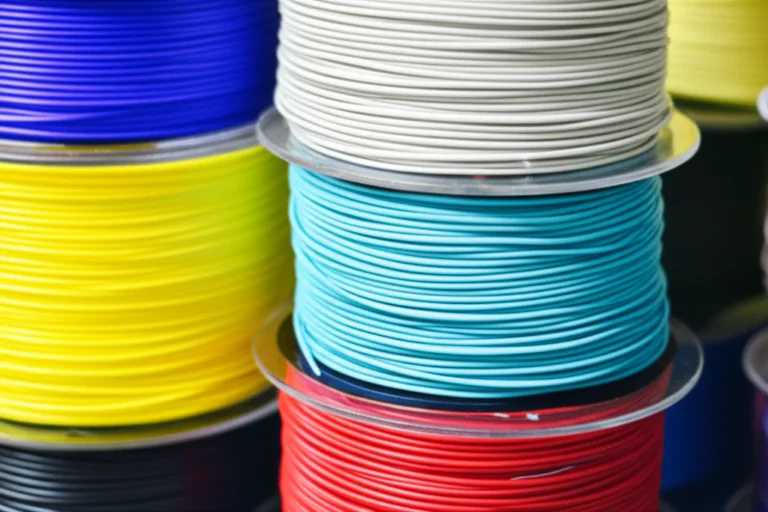
4. Material Matters: The True Cost of Filament, Resin, and Powders
Your printer is hungry, and you have to feed it. Material costs are the most significant ongoing expense.
- FDM Filaments: Standard PLA and PETG are quite affordable. But then you discover the wonderful world of exotic filaments. Wood-fill, glow-in-the-dark, carbon fiber-reinforced nylon, flexible TPU… each one comes with a higher price tag. A spool of engineering-grade material can easily cost two to four times as much as basic PLA.
- SLA Resins: Liquid resin is generally more expensive per kilogram than standard filament. “Tough” or “Flexible” engineering resins from brands like Siraya Tech or Formlabs command a premium for their advanced properties.
- SLS Powders: This is industrial territory. Nylon powder for SLS machines is bought in large quantities and is significantly more expensive than consumer materials.
👉 Shop for Popular 3D Printing Materials:
- PLA Filament: Amazon | Walmart
- PETG Filament: Amazon | Walmart
- Standard 3D Printer Resin: Amazon | Walmart
5. Wear and Tear: Maintenance, Spare Parts, and Unexpected Breakdowns
Your printer is a mechanical device with moving parts, and those parts will eventually wear out. It’s not a matter of if, but when.
Common Consumables & Replacement Parts:
- Nozzles: These are cheap but critical. Abrasive filaments like carbon fiber or glow-in-the-dark will chew through a standard brass nozzle in no time, requiring a switch to hardened steel.
- Build Surfaces: PEI sheets, glass beds, and magnetic flex plates lose their adhesion over time and need replacement.
- FEP/ACF Film (Resin): The transparent film at the bottom of a resin vat clouds up or gets punctured and is a regular replacement item.
- Fans, Belts, and Bearings: These components are in constant motion and will eventually fail.
It’s always a good idea to have a small stock of spare parts on hand to avoid downtime when something inevitably gives out mid-project.
6. Software Savvy: Slicers, CAD, and the Digital Toolkit
The good news? The software ecosystem is rich with amazing, free options!
- Slicers: Programs like PrusaSlicer, UltiMaker Cura, and Bambu Studio are incredibly powerful and cost nothing. They take your 3D model and slice it into the layers your printer understands.
- CAD/Modeling: For designing your own parts, you can start with user-friendly, free tools like Tinkercad or get a free personal-use license for the powerhouse that is Autodesk Fusion 360.
While there are paid options like the Simplify3D slicer or professional CAD packages, you can get incredibly far without spending a dime. This is one area where you can definitely save money! Dive into our 3D Design Software section to learn more.
7. The Finishing Touch: Post-Processing Tools and Time
A print is rarely “done” when it comes off the build plate. This “hidden” cost is more about your time and a collection of small tools.
- FDM: You’ll need tools for removing supports (flush cutters, pliers, deburring tools), sanding supplies, primer, and paints if you want a finished look.
- SLA: This is a whole other level. You’ll need a wash and cure station (or separate containers with isopropyl alcohol and a UV lamp), nitrile gloves, safety glasses, and paper towels. The process is involved and requires care.
8. Powering Your Prints: Electricity Consumption
Let’s bust a myth: for most hobbyists, electricity cost is a minor factor. A typical desktop 3D printer uses about as much power as a standard desktop computer. While a 48-hour print will certainly add a bit to your utility bill, it’s usually not the budget-breaker you might fear. However, for a print farm running dozens of machines 24/7, these costs become significant.
🏭 Beyond the Hobby Bench: Industrial vs. Consumer 3D Printing Costs
This is where the numbers get truly wild. If you’ve ever gotten a quote from a 3D printing service and gasped, it’s because they’re likely not using a hobbyist printer.
9. Precision & Performance: Why Industrial Machines Command Top Dollar
Industrial machines from companies like Stratasys or those using HP’s Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technology are built for a different purpose: repeatability, reliability, and precision. They have heated build chambers, incredibly precise components, and sophisticated software that guarantees parts are made to spec every single time. This reliability is crucial for engineering and manufacturing applications.
As highlighted in the video from 100 Concepts, the cost difference is staggering. An MJF machine can cost “half-a-million dollars” or more. This initial investment has to be recouped, which is a major reason why service bureau quotes seem so high. As one commenter on the Prusa forums put it, “If the prices you are being quoted by different services in a competitive marketplace are comparable, then they probably are not outrageous.” They’re simply reflecting the cost of running professional-grade equipment.
10. Exotic Materials: Metal, Composites, and High-Performance Polymers
Industrial printing unlocks a universe of materials that are impossible to print on a desktop machine. We’re talking about:
- Metals: Stainless steel, titanium, aluminum.
- High-Performance Polymers: PEEK, PEKK, and ULTEM, which have incredible heat and chemical resistance for aerospace and medical applications.
- Composites: Carbon fiber-filled nylon for parts that are both strong and lightweight.
These materials are orders of magnitude more expensive than consumer plastics, further driving up the cost of industrial prints.
👻 The Stealthy Spenders: Hidden Costs You Might Not Expect
These are the costs that sneak up on you when you’re not looking. The little gremlins of your 3D printing budget.
11. The “Oops!” Factor: Failed Prints and Material Waste
Ah, the dreaded “spaghetti monster.” Every single one of us has walked in to find a bird’s nest of tangled filament instead of our masterpiece. A clogged nozzle, poor bed adhesion, a random power flicker—it happens. Each failure is wasted filament or resin and lost time. Professional services have to bake the cost of potential failures into their pricing models. As the Prusa forum discussion notes, a service has to spend non-trivial time (perhaps half an hour) just to review and slice a model, and that’s before a single layer is printed.
12. The Upgrade Bug: Modifications and Accessories
Your printer works fine, but… what if it were better? The “upgrade bug” is real. You start with a simple printed fan shroud. Soon you’re eyeing an all-metal hotend from E3D, a direct-drive extruder, a BLTouch for perfect first layers, or a Raspberry Pi to run OctoPrint for remote monitoring. These upgrades are fun and can genuinely improve your printer’s performance, but they add up quickly!
13. Safety First: Essential Gear for a Healthy Workspace
Don’t skimp on safety!
- Ventilation: Printing with materials like ABS and ASA, or working with resin, releases Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). An enclosure with proper ventilation to the outside is highly recommended.
- Resin Safety: Nitrile gloves and safety glasses are non-negotiable when handling liquid resin to prevent skin irritation and chemical burns.
- Fire Safety: These are machines that heat up to high temperatures and are often left running unattended. A smoke detector above your printer and a nearby fire extinguisher are essential, common-sense precautions.
📉 The Great Debate: Is 3D Printing Truly Getting Cheaper?
Yes! Emphatically, yes. While it can still feel expensive, the cost of entry has plummeted over the last decade.
Technological Leaps & Market Competition
Fierce competition between brands like Creality, Elegoo, Sovol, and now Bambu Lab has been fantastic for consumers. Each company tries to one-up the others by offering more features for less money. Features that were once premium, like auto bed leveling and magnetic build plates, are now standard on entry-level machines.
The Open-Source Revolution’s Impact
The spirit of the open-source RepRap project lives on. Most consumer printers run on open-source firmware like Marlin, and as we mentioned, the best slicer software is free. This collaborative, community-driven development keeps costs down and innovation high.
🎯 When Does the Investment Pay Off? The Value Proposition of Additive Manufacturing
So, after all this talk of cost, is it even worth it? For us, the answer is a resounding YES. The key is to shift your thinking from “cost” to “value.”
Prototyping Powerhouse: Speeding Up Innovation
This is the killer app for 3D printing. As the video from 100 Concepts powerfully argues, 3D printing allows innovators to bypass the insane tooling costs of traditional manufacturing. Being able to design a part, print it overnight, test it the next day, and make revisions is a superpower. It accelerates development cycles from months to days. When you support innovators who use this tech, you’re “supporting companies that are actively trying to innovate.”
Customization King: Tailored Solutions for Every Need
The true magic of 3D printing is the ability to create one-of-a-kind objects.
- Need a specific bracket for a home repair that you can’t buy anywhere? Print it.
- Want to design a custom ergonomic grip for your game controller? You can.
- Looking for unique miniatures for your D&D campaign? The world of 3D Printable Objects is at your fingertips.
You can create solutions perfectly tailored to your needs, something mass production can never offer.
Education & Exploration: Learning the Future
A 3D printer is an incredible educational tool. It teaches design, engineering, problem-solving, and patience (so much patience). It’s a hands-on way to engage with technology and bring digital concepts into the physical world, making it a cornerstone of modern 3D Printing in Education.
Small-Batch Superpower: Manufacturing on Demand
For small businesses, Etsy sellers, and entrepreneurs, 3D printing is a revolution. It allows for “manufacturing on demand” with zero inventory. You can sell a product and only print it once an order comes in, eliminating the financial risk of a large production run.
💡 Smart Spending: Practical Strategies to Slash Your 3D Printing Costs
Ready to print without breaking the bank? Here are our team’s favorite tips for being a frugal maker.
Choosing Your Steed Wisely: Budget-Friendly Printer Selection
You don’t need a top-of-the-line machine to get started. Printers like the Sovol SV06 or the venerable Creality Ender 3 V3 SE offer fantastic performance for their price. Do your research, read reviews, and buy the printer that fits your budget and needs, not just the one with the most hype.
Material Mastery: Buying Smart and Storing Right
- Buy in Bulk: If you find a filament you love, consider buying multiple spools to get a bulk discount.
- Dry Your Filament: Wet filament is a primary cause of print failures. A simple filament dryer (or a modified food dehydrator) is a small investment that can save you spools of material in the long run.
- Don’t Overpay for Brands: While there are premium brands, many budget-friendly filament companies like Sunlu or eSun produce excellent quality material.
Preventative Care: Extending Your Printer’s Lifespan
A little maintenance goes a long way. Regularly check your belt tension, clean your guide rods, and inspect your wiring. Taking care of your machine will prevent costly breakdowns down the line.
Optimizing for Economy: Slicer Settings That Save
Your slicer is your best friend for saving material.
- Reduce Infill: Do you really need that decorative part to be 40% infill? For non-structural parts, 10-15% is often plenty.
- Use Smart Infill: Slicers like PrusaSlicer and Cura have “lightning” or “adaptive cubic” infill patterns that use material only where it’s needed to support the top surfaces, saving a huge amount of plastic.
- Avoid Supports (When Possible): Orient your model on the build plate to minimize overhangs and reduce the need for wasteful support structures.
DIY & Community: Leveraging Free Resources
The 3D printing community is one of the most generous out there.
- Free Models: Websites like Thingiverse, Printables, and MyMiniFactory have millions of free models, so you don’t always have to design from scratch.
- Get Help: If you’re stuck, forums on Reddit (like r/3Dprinting), Discord servers, and Facebook groups are filled with experienced users who are happy to help you troubleshoot for free.
✅ Conclusion: Is the Price Tag Justified?
After our deep dive into the multifaceted world of 3D printing costs, one thing is crystal clear: 3D printing is expensive because it’s a complex blend of cutting-edge technology, materials science, and skilled craftsmanship — all wrapped in a package that’s still evolving. Whether you’re a hobbyist printing miniatures or a business prototyping aerospace parts, the price you pay reflects the innovation, precision, and support behind the scenes.
We’ve seen how the initial investment in a printer is just the tip of the iceberg. Materials, maintenance, failed prints, and upgrades all chip away at your budget. But here’s the silver lining: the value you get — from rapid prototyping to custom creations — often far outweighs the costs.
If you’re just starting out, consider printers like the Creality Ender 3 V3 SE or Sovol SV06 for a budget-friendly entry point with solid performance. For those craving ultra-fine detail, resin printers like the Elegoo Mars 3 Pro offer incredible quality but come with higher material and post-processing costs. Industrial-grade machines and exotic materials are a whole different ballgame, reserved for specialized applications and budgets.
Remember the question we teased earlier: Is 3D printing truly getting cheaper? The answer is a cautious yes. Competition and open-source innovation have driven prices down dramatically, but the technology’s inherent complexity and material science keep a floor on costs. So, while you can print more affordably than ever, expect to invest time and care to maximize your value.
In short: 3D printing’s price tag is justified, but savvy users can tame costs with smart choices, community knowledge, and a bit of patience. Ready to join the revolution? Your next print awaits!
🔗 Recommended Links: Your Next Steps in Affordable 3D Printing
CHECK PRICE on Popular 3D Printers:
- Creality Ender 3 V3 SE: Amazon | Walmart | Creality Official Website
- Sovol SV06: Amazon | Walmart | Sovol Official Website
- Elegoo Mars 3 Pro (Resin Printer): Amazon | Walmart | Elegoo Official Website
👉 Shop 3D Printing Materials:
- PLA Filament: Amazon | Walmart
- PETG Filament: Amazon | Walmart
- Standard 3D Printer Resin: Amazon | Walmart
Recommended Books on 3D Printing:
- 3D Printing Failures: How to Diagnose and Repair All Desktop 3D Printing Issues by Sean Aranda — Amazon
- 3D Printing: The Next Industrial Revolution by Christopher Barnatt — Amazon
- Make: 3D Printing: The Essential Guide to 3D Printers by Anna Kaziunas France — Amazon
❓ FAQ: Burning Questions About 3D Printing Costs Answered
What factors contribute to the high cost of 3D printing materials?
3D printing materials vary widely in price due to their composition, manufacturing process, and performance characteristics. Basic filaments like PLA are made from abundant bioplastics and are relatively cheap. However, specialty filaments infused with carbon fiber, metal powders, or flexible polymers require complex manufacturing and quality control, driving prices up. Resin materials often include proprietary chemical formulations that provide strength, flexibility, or heat resistance, increasing cost. Industrial powders for SLS or metal printing are even more expensive due to purity and processing requirements. Additionally, packaging and storage to prevent moisture contamination add to expenses.
Read more about “3D Printing Market Share in 2025: Who’s Leading the Revolution? 🚀”
How does the complexity of a design affect 3D printing expenses?
Complex designs often require longer print times, more support structures, and higher failure risk, all of which increase costs. Intricate geometries may need slower print speeds to maintain quality, consuming more electricity and machine hours. Supports add material waste and post-processing labor. Complex models are also more challenging to slice and may require multiple iterations to perfect, increasing operator time. As noted by users on the Prusa forums, the time spent reviewing and preparing models is a significant cost factor for service providers, which translates into higher prices for complex prints.
Read more about “How Much Does It Cost to Make a 3D Image? 💰 10 Essential Insights …”
Are there affordable alternatives to reduce 3D printing costs?
Absolutely! Here are some strategies:
- Print Yourself: Owning a hobbyist printer dramatically reduces per-part costs compared to services.
- Optimize Designs: Simplify geometry, reduce infill, and orient models to minimize supports.
- Use Budget Materials: Standard PLA or PETG filaments are affordable and versatile.
- Leverage Free Software: Use free slicers and CAD tools to avoid software expenses.
- Buy Materials in Bulk: Purchasing filament spools or resin in larger quantities often yields discounts.
- Community Resources: Download free models from sites like Thingiverse and seek advice from online forums to avoid costly trial-and-error.
Read more about “75 Most Useful 3D Printed Objects for Students (2025) 🎓”
Why do professional 3D printers cost more than consumer models?
Professional 3D printers incorporate advanced hardware, industrial-grade components, and proprietary technologies that ensure higher precision, reliability, and repeatability. They often feature heated build chambers, multi-material capabilities, and enhanced safety systems. These machines undergo rigorous quality control and come with dedicated support and warranties. Additionally, they are designed to handle exotic materials like metals and engineering polymers, which require specialized hardware such as high-power lasers or inert gas environments. The cost of developing, manufacturing, and maintaining these sophisticated systems is reflected in their premium price tags.
How do failed prints impact overall 3D printing costs?
Failed prints waste both material and time, which can be costly especially with expensive filaments or resins. Troubleshooting failures requires additional operator time and sometimes replacement parts. For service providers, the risk of failure is factored into pricing to cover potential reprints and labor. Hobbyists can mitigate this by fine-tuning printer settings, maintaining equipment, and using reliable materials.
What role does maintenance play in the cost of 3D printing?
Regular maintenance extends the life of your printer and reduces unexpected downtime and repair costs. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly part replacements or complete machine failure. Budgeting for consumables like nozzles, belts, and build surfaces is essential to avoid surprises.
📚 Reference Links: Dive Deeper into the Data
- Prusa3D Forum Discussion on 3D Printing Service Costs: Why are 3D printing services so outrageously expensive?
- 100 Concepts Video on 3D Printing History and Costs: YouTube – 3D Printing Explained (Note: Replace with actual URL if available)
- RepRap Open Source Project: reprap.org
- Creality Official Website: creality.com
- Prusa Research Official Website: prusa3d.com
- Bambu Lab Official Website: bambulab.com
- Elegoo Official Website: elegoo.com
- Sovol Official Website: sovol3d.com
- Siraya Tech Resins: siraya.tech
- Autodesk Fusion 360: autodesk.com/products/fusion-360
- OctoPrint Remote Monitoring: octoprint.org
- Facebook Discussion on Resin Printer Costs: Why are resin printers so expensive?
Thanks for joining us on this deep dive into why 3D printing can be so expensive. Remember, knowledge is your best tool to turn that sticker shock into smart spending and creative success. Happy printing! 🚀