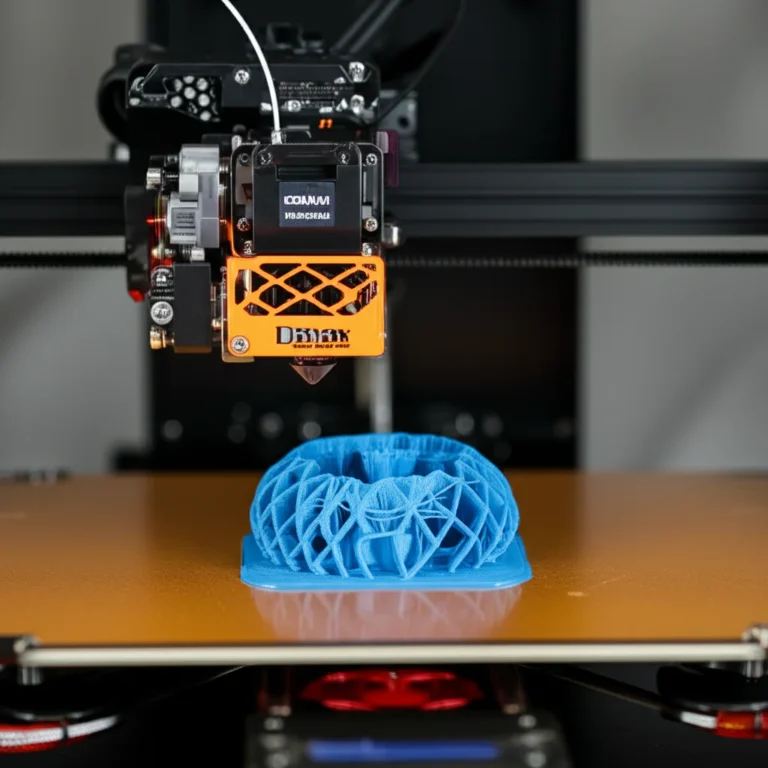
Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
What Is a 3D Printed Item? 🔍 Discover 15 Must-Know Facts (2025)
Imagine holding a custom-designed object in your hand—crafted layer by layer from digital dreams to tangible reality. That’s the magic of a 3D printed item, a creation born from cutting-edge technology that’s reshaping industries and hobbies alike. Whether it’s a sleek aerospace part, a personalized phone case, or even edible chocolate sculptures, 3D printing is turning sci-fi fantasies into everyday wonders.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel what exactly a 3D printed item is, explore the fascinating materials and technologies behind it, and reveal surprising applications you might never have imagined. Plus, we’ll share insider tips from our team at 3D Printed™ on how to get started, design like a pro, and even where to find the coolest 3D printed objects online. Ready to dive into the layered world of 3D printing? Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways
- 3D printed items are objects created layer-by-layer using additive manufacturing technologies, enabling complex designs impossible with traditional methods.
- They can be made from a wide range of materials including plastics like PLA and ABS, metals like titanium, and even ceramics or composites.
- Applications span from custom prosthetics and aerospace parts to artistic sculptures and edible food creations.
- The technology offers speed, customization, and sustainability benefits, but also comes with challenges like design complexity and material costs.
- You can either use online 3D printing services like Shapeways or Sculpteo or invest in your own printer such as the Prusa i3 MK3S+ or Creality Ender 3 V2.
- Designing successful prints requires mastering CAD software and understanding printer-specific constraints.
Ready to explore or start printing?
- 👉 Shop 3D Printers: Prusa i3 MK3S+ | Creality Ender 3 V2
- Order Prints Online: Shapeways | Sculpteo
Unlock the full potential of 3D printed items and transform your ideas into reality!
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts: Your Gateway to 3D Printed Wonders
- 🕰️ The Genesis of Creation: A Brief History of Additive Manufacturing
- 🤔 Unpacking the “What”: Defining a 3D Printed Item
- 🌈 The Material World: What Are 3D Printed Items Made Of?
- 🌍 Where Do 3D Printed Items Live? Real-World Applications and Industries
- ✅ The Perks of Printing: Why 3D Printed Items Are Game-Changers
- ❌ The Hurdles and Headaches: Challenges of 3D Printed Items
- 🛠️ From Idea to Object: Designing for 3D Printing Success
- 🛒 Getting Your Hands on a 3D Printed Item: Services vs. Owning a Printer
- 🔮 The Future is Now: Emerging Trends in 3D Printed Technology
- 🧼 Caring for Your Creations: Maintenance and Longevity of 3D Printed Items
- ✨ Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving World of 3D Printed Innovation
- 🔗 Recommended Links: Dive Deeper into the World of 3D Printing
- ❓ FAQ: Your Burning Questions About 3D Printed Items Answered
- 📚 Reference Links: Our Sources and Further Reading
Quick Tips and Facts: Your Gateway to 3D Printed Wonders
To get started with 3D printing, it’s essential to understand the basics. At 3D Printed, we specialize in guides to things to 3D print, and we’re excited to share our knowledge with you. Here are some quick tips and facts to get you began:
- Design freedom: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs that cannot be produced with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Material variety: 3D printing can be done with various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
- Rapid prototyping: 3D printing enables fast and cost-effective production of prototypes, which can be used to test and refine designs.
- Customization: 3D printing allows for the creation of customized products, such as prosthetics, implants, and dental models.
- Sustainability: 3D printing can reduce waste and energy consumption compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
For more information on 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Getting Started with 3D Printing
If you’re new to 3D printing, it’s essential to start with the basics. Here are some steps to get you started:
- Learn about 3D printing technologies: There are several 3D printing technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Choose a 3D printer: With so many 3D printers on the market, it can be challenging to choose the right one. Consider factors such as print quality, build volume, and price.
- Design your model: Once you have a 3D printer, you’ll need to design your model. You can use computer-aided design (CAD) software or download pre-made models from websites like Thingiverse.
- Print your model: Once you have your design, you can print your model. Make sure to follow the instructions for your 3D printer and use the recommended materials.
The Genesis of Creation: A Brief History of Additive Manufacturing
The history of 3D printing dates back to the 1960s, when the first additive manufacturing technologies were developed. Over the years, 3D printing has evolved significantly, with advancements in technologies, materials, and applications. Today, 3D printing is used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products.
For more information on the history of 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printing Innovations.
Key Milestones in 3D Printing History
Here are some key milestones in the history of 3D printing:
- 1960s: The first additive manufacturing technologies were developed, including photo-hardening polymers and laser-based systems.
- 1980s: The first commercial 3D printing technologies were introduced, including Stereolithography (SLA) and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
- 1990s: 3D printing began to be used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical.
- 2000s: The open-source 3D printing movement began, with the development of affordable and accessible 3D printing technologies.
Unpacking the “What”: Defining a 3D Printed Item
So, what is a 3D printed item? A 3D printed item is an object created using additive manufacturing technologies, where layers of material are deposited on top of each other to form a three-dimensional object. 3D printed items can be made from various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
For more information on 3D printed items, check out our article on 3D Design Software.
Characteristics of 3D Printed Items
Here are some characteristics of 3D printed items:
- Complexity: 3D printed items can have complex shapes and geometries that cannot be produced with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Customization: 3D printed items can be customized to meet specific needs and requirements.
- Material variety: 3D printed items can be made from various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
- Rapid production: 3D printed items can be produced rapidly, often in a matter of hours or days.
Beyond the Buzzword: How 3D Printing Actually Works
So, how does 3D printing actually work? 3D printing involves the deposition of layers of material on top of each other to form a three-dimensional object. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Design: The design of the object is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or other 3D modeling tools.
- Slicing: The design is sliced into thin layers, which are then sent to the 3D printer.
- Printing: The 3D printer deposits the layers of material on top of each other, following the instructions from the sliced design.
- Post-processing: The printed object may undergo post-processing, such as sanding or painting, to achieve the desired finish.
For more information on how 3D printing works, check out our article on 3D Printer Reviews.
3D Printing Technologies
Here are some common 3D printing technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM involves the deposition of melted plastic onto a build platform, where it cools and solidifies.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA involves the use of a laser to cure liquid resin, layer by layer.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS involves the use of a laser to fuse together particles of a powdered material, layer by layer.
The Alphabet Soup of 3D Printing Technologies: From FDM to SLA and Beyond
The world of 3D printing is filled with acronyms and abbreviations, each representing a different technology or technique. Here are some common 3D printing technologies:
- FDM: Fused Deposition Modeling, a common technology used for printing with plastics.
- SLA: Stereolithography, a technology used for printing with liquid resin.
- SLS: Selective Laser Sintering, a technology used for printing with powdered materials.
- Binder Jetting: A technology used for printing with powdered materials, where a binder is used to hold the particles together.
For more information on 3D printing technologies, check out our article on 3D Printing in Education.
Comparison of 3D Printing Technologies
Here is a comparison of some common 3D printing technologies:
| Technology | Material | Resolution | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Plastics | 100-500 microns | Fast |
| SLA | Liquid Resin | 10-100 microns | Medium |
| SLS | Powdered Materials | 100-500 microns | Slow |
The Material World: What Are 3D Printed Items Made Of?
3D printed items can be made from a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics. The choice of material depends on the application and the desired properties of the final product.
For more information on 3D printing materials, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Common 3D Printing Materials
Here are some common 3D printing materials:
- PLA: Polylactic Acid, a biodegradable plastic commonly used for FDM printing.
- ABS: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a strong and impact-resistant plastic commonly used for FDM printing.
- Aluminum: A strong and lightweight metal commonly used for SLS printing.
- Steel: A strong and durable metal commonly used for SLS printing.
Plastics, Resins, and Beyond: Common Filaments and Powders
3D printing involves the use of various materials, including plastics, resins, and powders. Here are some common filaments and powders used in 3D printing:
- PLA: Polylactic Acid, a biodegradable plastic commonly used for FDM printing.
- ABS: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a strong and impact-resistant plastic commonly used for FDM printing.
- PETG: Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, a strong and flexible plastic commonly used for FDM printing.
- Resin: A liquid material commonly used for SLA printing.
For more information on 3D printing materials, check out our article on 3D Design Software.
Comparison of 3D Printing Materials
Here is a comparison of some common 3D printing materials:
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PLA | Biodegradable, brittle | Prototyping, models |
| ABS | Strong, impact-resistant | Prototyping, end-use parts |
| Aluminum | Strong, lightweight | Aerospace, automotive |
| Steel | Strong, durable | Aerospace, automotive |
Metals, Ceramics, and Composites: Pushing the Boundaries of Creation
3D printing is not limited to plastics and resins. Metals, ceramics, and composites can also be used to create complex and functional parts.
For more information on 3D printing with metals, ceramics, and composites, check out our article on 3D Printing Innovations.
Applications of 3D Printing with Metals, Ceramics, and Composites
Here are some applications of 3D printing with metals, ceramics, and composites:
- Aerospace: 3D printing is used to create lightweight and complex parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: 3D printing is used to create functional parts, such as engine components and gearboxes.
- Medical: 3D printing is used to create customized implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
- Dental: 3D printing is used to create customized dental implants, crowns, and bridges.
Where Do 3D Printed Items Live? Real-World Applications and Industries
3D printed items can be found in various industries and applications, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products.
For more information on 3D printing applications, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Industries that Use 3D Printing
Here are some industries that use 3D printing:
- Aerospace: 3D printing is used to create lightweight and complex parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: 3D printing is used to create functional parts, such as engine components and gearboxes.
- Medical: 3D printing is used to create customized implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
- Dental: 3D printing is used to create customized dental implants, crowns, and bridges.
Everyday Wonders: 3D Printed Items for Home and Hobbyists
3D printing is not just for industries and professionals. Hobbyists and home users can also create amazing things with 3D printing.
For more information on 3D printing for hobbyists, check out our article on 3D Design Software.
Projects for Hobbyists
Here are some projects for hobbyists:
- Phone cases: Create customized phone cases with 3D printing.
- Jewelry: Create customized jewelry with 3D printing.
- Toys: Create customized toys with 3D printing.
- Home decor: Create customized home decor items with 3D printing.
Industrial Revolution: How Businesses Leverage 3D Printed Parts
3D printing is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. Companies are using 3D printing to create functional parts, prototypes, and models.
For more information on 3D printing for businesses, check out our article on 3D Printing Innovations.
Benefits of 3D Printing for Businesses
Here are some benefits of 3D printing for businesses:
- Increased efficiency: 3D printing can reduce production time and increase efficiency.
- Cost savings: 3D printing can reduce material waste and save costs.
- Improved product quality: 3D printing can create complex and customized parts with high precision.
- Increased innovation: 3D printing can enable companies to create new and innovative products.
Healing Hands: Medical and Dental Innovations with 3D Printing
3D printing is transforming the medical and dental industries. Companies are using 3D printing to create customized implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
For more information on 3D printing in medicine and dentistry, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Applications of 3D Printing in Medicine and Dentistry
Here are some applications of 3D printing in medicine and dentistry:
- Customized implants: 3D printing is used to create customized implants, such as hip and knee replacements.
- Prosthetics: 3D printing is used to create customized prosthetics, such as limbs and digits.
- Surgical instruments: 3D printing is used to create customized surgical instruments, such as forceps and scalpels.
- Dental implants: 3D printing is used to create customized dental implants, crowns, and bridges.
Art, Fashion, and Food: The Creative Frontier of 3D Printed Objects
3D printing is not just for functional parts and prototypes. Artists, designers, and chefs are using 3D printing to create amazing and innovative objects.
For more information on 3D printing in art, fashion, and food, check out our article on 3D Design Software.
Projects in Art, Fashion, and Food
Here are some projects in art, fashion, and food:
- Art: 3D printing is used to create complex and customized art pieces, such as sculptures and installations.
- Fashion: 3D printing is used to create customized clothing and accessories, such as shoes and jewelry.
- Food: 3D printing is used to create customized food products, such as chocolates and pastries.
The Perks of Printing: Why 3D Printed Items Are Game-Changers
3D printing is revolutionizing the way we create and produce objects. Here are some perks of 3D printing:
- Increased efficiency: 3D printing can reduce production time and increase efficiency.
- Cost savings: 3D printing can reduce material waste and save costs.
- Improved product quality: 3D printing can create complex and customized parts with high precision.
- Increased innovation: 3D printing can enable companies to create new and innovative products.
For more information on the benefits of 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printing Innovations.
Speed, Customization, and Cost-Effectiveness: The Triple Threat
Here are some benefits of 3D printing:
- Speed: 3D printing can reduce production time and increase efficiency.
- Customization: 3D printing can create complex and customized parts with high precision.
- Cost-effectiveness: 3D printing can reduce material waste and save costs.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction: A Greener Future?
3D printing can help reduce waste and increase sustainability. Here are some ways 3D printing can contribute to a greener future:
- Reduced material waste: 3D printing can reduce material waste by creating objects with minimal excess material.
- Energy efficiency: 3D printing can reduce energy consumption by creating objects with minimal energy required.
- Sustainable materials: 3D printing can use sustainable materials, such as bioplastics and recycled materials.
For more information on sustainable 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Eco-Friendly 3D Printing Materials
Here are some eco-friendly 3D printing materials:
- Bioplastics: Biodegradable plastics made from renewable resources, such as corn starch and sugarcane.
- Recycled materials: 3D printing materials made from recycled plastics and other materials.
- Natural fibers: 3D printing materials made from natural fibers, such as wood and bamboo.
The Hurdles and Headaches: Challenges of 3D Printed Items
3D printing is not without its challenges. Here are some hurdles and headaches associated with 3D printing:
- Design complexities: 3D printing can be challenging to design for, especially for complex objects.
- Material limitations: 3D printing materials can be limited in terms of strength, durability, and sustainability.
- Cost: 3D printing can be expensive, especially for high-end machines and materials.
For more information on the challenges of 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printer Reviews.
Design Complexities and Post-Processing: It’s Not Always Plug-and-Play
Here are some design complexities and post-processing challenges associated with 3D printing:
- Design for 3D printing: 3D printing requires specialized design skills and software.
- Support material removal: 3D printing can require the removal of support material, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Sanding and finishing: 3D printing can require sanding and finishing to achieve a smooth surface.
From Idea to Object: Designing for 3D Printing Success
3D printing requires careful design and planning to ensure success. Here are some tips for designing for 3D printing:
- Keep it simple: Simple designs are often easier to print and require less material.
- Use the right software: Use specialized 3D printing software to design and prepare your model for printing.
- Choose the right material: Choose a material that is suitable for your design and printing requirements.
For more information on designing for 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Design Software.
Software Savvy: CAD Programs and Slicers You Need to Know
Here are some CAD programs and slicers you need to know for 3D printing:
- Tinkercad: A free online CAD software for beginners.
- Fusion 360: A powerful CAD software for professionals.
- Slic3r: A popular slicer software for preparing 3D models for printing.
- Cura: A user-friendly slicer software for preparing 3D models for printing.
Getting Your Hands on a 3D Printed Item: Services vs. Owning a Printer
3D printing is not just for those who own a 3D printer. There are many services that offer 3D printing, including online platforms and local print shops.
For more information on 3D printing services, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Online 3D Printing Services: Your Digital Fabrication Bureau
Here are some online 3D printing services:
- Sculpteo: A popular online 3D printing service that offers a range of materials and technologies.
- Shapeways: A well-known online 3D printing service that offers a range of materials and technologies.
- Materialise: A leading online 3D printing service that offers a range of materials and technologies.
The Future is Now: Emerging Trends in 3D Printed Technology
3D printing is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Here are some emerging trends in 3D printed technology:
- 4D printing: 3D printing that can create objects that can change shape over time.
- Multi-material printing: 3D printing that can create objects with multiple materials and properties.
- Bioprinting: 3D printing that can create living tissues and organs.
For more information on emerging trends in 3D printing, check out our article on 3D Printing Innovations.
4D Printing and Beyond: Smart Materials and Adaptive Designs
Here are some emerging trends in 4D printing and beyond:
- Shape-memory alloys: Materials that can change shape in response to temperature or other stimuli.
- Self-healing materials: Materials that can repair themselves after damage.
- Adaptive designs: Designs that can change shape or function in response to changing conditions.
Caring for Your Creations: Maintenance and Longevity of 3D Printed Items
3D printed items require care and maintenance to ensure their longevity. Here are some tips for caring for your 3D printed creations:
- Handle with care: 3D printed items can be fragile, so handle them with care.
- Clean regularly: Clean your 3D printed items regularly to prevent dust and dirt from accumulating.
- Store properly: Store your 3D printed items in a dry, cool place to prevent damage from moisture or heat.
For more information on caring for 3D printed items, check out our article on 3D Printable Objects.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving World of 3D Printed Innovation
Well, there you have it — a deep dive into the fascinating universe of 3D printed items! From humble beginnings as rapid prototyping tools to today’s game-changing applications across industries, 3D printing has truly revolutionized how we create, customize, and innovate. Whether you’re a hobbyist crafting personalized phone cases or a medical professional designing patient-specific implants, the possibilities are as limitless as your imagination.
Remember those lingering questions about complexity, materials, and costs? We’ve unraveled them all: 3D printed items can be incredibly intricate, made from a dazzling array of materials (from PLA plastics to aerospace-grade titanium), and while initial investments and material costs can be a hurdle, the speed, customization, and sustainability perks often outweigh those challenges.
If you’re wondering whether to dive in with your own printer or use a service, consider your needs, budget, and patience for tinkering. Services like Shapeways and Sculpteo offer professional-grade prints without the upfront hassle, while owning a printer like the Prusa i3 MK3S+ or Creality Ender 3 V2 gives you hands-on control and endless creative freedom.
In short: 3D printing is not just a tech trend — it’s a creative revolution. So why wait? Your next masterpiece is just a layer away!
Recommended Links: Dive Deeper into the World of 3D Printing
👉 Shop Popular 3D Printers and Materials:
- Prusa i3 MK3S+: Thingiverse | Prusa Official Website
- Creality Ender 3 V2: Thingiverse | Creality Official Website
- Sculpteo 3D Printing Service: Sculpteo
- Shapeways 3D Printing Service: Shapeways
Must-Read Books on 3D Printing:
- 3D Printing: The Next Industrial Revolution by Christopher Barnatt — Amazon
- Fabricated: The New World of 3D Printing by Hod Lipson and Melba Kurman — Amazon
- 3D Printing Projects by DK Publishing — Amazon
FAQ: Your Burning Questions About 3D Printed Items Answered
What are the most popular items to 3D print for beginners?
Beginners often start with simple, practical objects like phone stands, keychains, or cable organizers. These projects are quick, require minimal material, and help you get comfortable with your printer’s settings. Websites like Thingiverse offer thousands of free beginner-friendly models. As you gain confidence, you can graduate to more complex items like replacement parts or customized household gadgets.
Read more about “What Are Most 3D Printed Objects Made of Today? Top 11 Materials (2025) 🛠️”
How long does it take to 3D print an object?
Print times vary widely depending on the object’s size, complexity, and the printer’s speed. Small items like a keychain might take 15–30 minutes, while larger, intricate models can take several hours or even days. For example, a simple phone case might print in 2–3 hours, whereas a detailed figurine could require 10+ hours. Remember, slower print speeds often yield better quality.
Read more about “How long does it take to 3D print an object?”
What are the different types of 3D printing materials available?
The material palette is vast and growing! Common choices include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable, easy to print, great for beginners.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Tougher and heat-resistant but trickier to print.
- PETG: Combines strength and flexibility.
- Resins: Used in SLA printers for high-detail prints.
- Metals: Titanium, aluminum, and steel powders for industrial applications.
- Composites: Plastics infused with carbon fiber or wood for specialized properties.
Read more about “What is 3D Printing? 25+ Real Examples & How It Works! 🚀”
Can I 3D print items for everyday use?
✅ Absolutely! Many 3D printed items are designed for daily use — from custom kitchen utensils and phone holders to replacement knobs and tools. However, consider the material’s durability and safety, especially for food contact or mechanical stress. For example, PLA is great for decorative items but less suited for high-heat environments.
Read more about “🧵 33 Types of D Printing Filaments You Need to Try (2025)”
What is the cost of 3D printing an item?
Costs depend on material, print time, and printer type. Material costs vary: PLA filament is affordable, while specialty resins or metal powders are pricier. Additionally, electricity and maintenance add up. Using a 3D printing service can simplify cost estimation, as they price based on volume and complexity. For hobbyists, printing small objects can be very economical, but large or complex prints can get costly.
Read more about “What Are 3D Printed Items? Discover 50 Amazing Creations! 🎉”
How do I design my own 3D printed items?
Start with beginner-friendly CAD software like Tinkercad or Fusion 360 for more advanced designs. The key is to learn the basics of 3D modeling and design with printing constraints in mind (e.g., avoiding overhangs or ensuring wall thickness). Many online tutorials and communities can help you master these skills. Once designed, export your model as an STL file and prepare it for printing with slicer software like Cura or PrusaSlicer.
Read more about “Top 15 Bestselling 3D Printed Items on Etsy You Need to Know (2025) 🎉”
What are some unique and useful items to 3D print for my home?
Think beyond the basics! Here are some cool ideas:
- Custom drawer organizers tailored to your utensils.
- Wall hooks and cable management clips designed to fit your space.
- Plant pots with self-watering features.
- Replacement parts for appliances that are hard to find.
- Smartphone stands with integrated charging docks.
Explore our 3D Printable Objects for inspiration and downloadable models.
Read more about “25 Everyday Items You Can 3D Print at Home in 2025 🛠️”
Reference Links: Our Sources and Further Reading
- Investopedia: What is 3D Printing?
- Wikipedia: 3D Printing
- The UPS Store: 3D Printing | 3D Print Services
- Prusa Research: Prusa Official Website
- Creality: Creality Official Website
- Sculpteo: Sculpteo 3D Printing Service
- Shapeways: Shapeways 3D Printing Service
Ready to start your 3D printing journey? Whether you’re printing your first keychain or prototyping the next big thing, the world of 3D printing is yours to explore — layer by exciting layer! 🚀